Monitoring Metric Details
Last updated:2026-01-20 17:02:41
Feature DescriptionFeature Description
TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) provides a comprehensive, multi-dimensional monitoring metric system, covering dimensions such as instances, topics, and consumer groups, and helping you monitor the operation status of resources in real time. This document introduces the meanings of various monitoring metrics of CKafka and the recommended key metrics to focus on. You can use these metrics to quickly master the health status of resources such as instances, and determine whether to perform Ops operations, such as specification adjustment, to ensure stable operation.TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) provides a comprehensive, multi-dimensional monitoring metric system, covering dimensions such as instances, topics, and consumer groups, and helping you monitor the operation status of resources in real time. This document introduces the meanings of various monitoring metrics of CKafka and the recommended key metrics to focus on. You can use these metrics to quickly master the health status of resources such as instances, and determine whether to perform Ops operations, such as specification adjustment, to ensure stable operation.
NamespaceNamespace
Namespace=QCE/CKAFKANamespace=QCE/CKAFKACluster Health Status DescriptionCluster Health Status Description
CKafka clusters have three health statuses: Healthy, Alarm, and Abnormal. The system periodically inspects each cluster. The inspection program checks metrics such as the number of connections, disk usage percentage, peak production bandwidth, and peak consumption bandwidth. When these metrics exceed specific thresholds, different health statuses are generated.CKafka clusters have three health statuses: Healthy, Alarm, and Abnormal. The system periodically inspects each cluster. The inspection program checks metrics such as the number of connections, disk usage percentage, peak production bandwidth, and peak consumption bandwidth. When these metrics exceed specific thresholds, different health statuses are generated.
If a cluster status becomes abnormal, you can go to the monitoring page in the console to view the corresponding monitoring metric details to troubleshoot the issue. If you have further requirements such as viewing cluster load monitoring, you can go to the Advanced Monitoring page to view relevant information. If a cluster status becomes abnormal, you can go to the monitoring page in the console to view the corresponding monitoring metric details to troubleshoot the issue. If you have further requirements such as viewing cluster load monitoring, you can go to the Advanced Monitoring page to view relevant information. Only Pro Edition instances support the advanced monitoring feature.Only Pro Edition instances support the advanced monitoring feature.
MetricMetric | Threshold (N)Threshold (N) | Status DescriptionStatus Description |
Number of connections (default maximum value: 50000)Number of connections (default maximum value: 50000) | N ≤ 80% N ≤ 80% | HealthyHealthy |
| 80% < N ≤ 95% 80% < N ≤ 95% | AlarmAlarm |
| N > 95% N > 95% | AbnormalAbnormal |
Disk usage percentageDisk usage percentage | N ≤ 80%N ≤ 80% | HealthyHealthy |
| 80% < N ≤ 95%80% < N ≤ 95% | AlarmAlarm |
| N > 95%N > 95% | AbnormalAbnormal |
Peak production bandwidth (excluding replica bandwidth)Peak production bandwidth (excluding replica bandwidth) | N ≤ 80%N ≤ 80% | HealthyHealthy |
| 80% < N ≤ 100%80% < N ≤ 100% | AlarmAlarm |
| N > 100%N > 100% | AbnormalAbnormal |
Peak consumption bandwidthPeak consumption bandwidth | N ≤ 80%N ≤ 80% | HealthyHealthy |
| 80% < N ≤ 100%80% < N ≤ 100% | AlarmAlarm |
| N > 100%N > 100% | AbnormalAbnormal |
Note:Note:
The default maximum number of connections is 50000. Threshold judgment is based on a percentage of this maximum value. If the number of connections of an instance exceeds the maximum value, clients cannot create new connections. If this maximum value does not meet your business requirements, you can The default maximum number of connections is 50000. Threshold judgment is based on a percentage of this maximum value. If the number of connections of an instance exceeds the maximum value, clients cannot create new connections. If this maximum value does not meet your business requirements, you can contact uscontact us to request a quota increase. to request a quota increase.
Basic Monitoring MetricsBasic Monitoring Metrics
CKafka's basic monitoring capability supports monitoring metrics in three dimensions: instance, topic, and consumer group. It is suitable for basic Ops scenarios such as assisting with exception detection and cluster capacity planning. The following tables describe all monitoring metrics provided by CKafka's basic monitoring capability. Configure monitoring and alarm policies appropriately based on your business requirements.CKafka's basic monitoring capability supports monitoring metrics in three dimensions: instance, topic, and consumer group. It is suitable for basic Ops scenarios such as assisting with exception detection and cluster capacity planning. The following tables describe all monitoring metrics provided by CKafka's basic monitoring capability. Configure monitoring and alarm policies appropriately based on your business requirements.
Note:Note:
The content in the following tables is consistent with Tencent Cloud Observability Platform (TCOP) to ensure data consistency during reporting and alarming. Certain time granularities are not displayed in the CKafka console. You can view detailed data in TCOP.The content in the following tables is consistent with Tencent Cloud Observability Platform (TCOP) to ensure data consistency during reporting and alarming. Certain time granularities are not displayed in the CKafka console. You can view detailed data in TCOP.
Metric Name | Unit | Description |
InstanceMaxProFlow | MB | Peak bandwidth of message production for a single replica in an instance, excluding the bandwidth generated by replicas. The metric is used as a reference for calculating the instance production bandwidth usage percentage. The maximum value is taken over the unit time period. |
InstanceProFlow | MB | Production traffic of an instance (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
Instance Production Bandwidth Percentage | % | Percentage of instance production bandwidth relative to the quota. The average value is taken over the unit time period. |
InstanceMaxConFlow | MB | Peak bandwidth of message consumption for an instance. There is no replica concept during consumption. The metric is used as a reference for calculating the instance consumption bandwidth usage percentage. The maximum value is taken over the unit time period. |
InstanceConFlow | MB | Consumption traffic of an instance (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
Instance Consumption Bandwidth Percentage | % | Percentage of instance consumption bandwidth relative to the quota. The average value is taken over the unit time period. |
InstanceProCount | Count | Number of produced messages for an instance. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
InstanceConCount | Count | Number of consumed messages for an instance. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
InstanceMsgCount | Count | Total number of messages persisted to disks for an instance (excluding replicas). The latest value is taken according to the selected time granularity. |
InstanceTps | Count/s | Message request rate of a cluster instance, including production, consumption, metadata, and offset commit requests. The average value is taken over the unit time period. |
BMetadataRequestsPersecOneminuterate BProduceRequestsPersecOneminuterate BFetchConsumerRequestsPersecOneminuterate BOffsetCommitRequestsPersecOneminuterate | Count/s | Cluster TPS changes. The average value is taken over the unit time period. |
InstanceDiskUsage | MB | Disk usage of an instance (including replicas). The latest value is taken according to the selected time granularity. |
DiskUtilization | % | Percentage of the current disk usage relative to the total disk capacity of the instance specifications. The average value is taken over the unit time period. |
InstanceProduceThrottle | Count | Number of production traffic throttling events for an instance. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
InstanceConsumeThrottle | Count | Number of consumption traffic throttling events for an instance. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
InstanceMaxNodeConnection | Count | Number of connections for all broker nodes in the current instance. The maximum value is taken according to the selected time granularity. |
InstanceConnection | Count | Number of connections for all broker nodes in the current instance. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
Topic monitoringTopic monitoring
Metric Name | Unit | Description |
topic maximum produce flow | MB/s | Maximum production traffic of a topic (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). The maximum value is taken according to the selected time granularity. |
topic maximum consumer flow | MB/s | Maximum consumption traffic of a topic. The maximum value is taken according to the selected time granularity. |
topic consume message count | Count | Actual number of consumed messages for a topic. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
topic consume flow | MB | Actual consumption traffic of a topic (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
topic message heap size | MB | Actual total disk space used by messages in a topic (excluding replicas). The latest value is calculated according to the selected time granularity. |
topic produce message count | Count | Actual number of produced messages for a topic. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
topic produce flow | MB | Actual production traffic of a topic (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
topic message heap count | Count | Actual total number of messages persisted to disks for a topic (excluding replicas). The latest value is taken according to the selected time granularity. |
topic consume throttle | Count/s | Number of consumption traffic throttling events of a topic. The average value is taken over the selected time granularity. |
topic produce throttle | Count/s | Number of production traffic throttling events of a topic. The average value is taken over the selected time granularity. |
Topic - Partition monitoringTopic - Partition monitoring
Metric Name | Unit | Description |
partition consume message count | Count | Actual number of consumed messages for a partition. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
partition consume flow | MB | Actual consumption traffic of a partition (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
partition message count | Count | Actual total number of messages persisted to disks for a partition (excluding replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
partition message heap | MB | Actual total disk space used by messages in a partition (excluding replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
partition produce message count | Count | Actual number of produced messages for a partition. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
partition produce flow | MB | Actual production traffic of a partition (excluding the traffic generated by replicas). It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
Consumer group - Topic monitoringConsumer group - Topic monitoring
Metric Name | Unit | Description |
topic consumegroup unconsume message count | Count | Total number of unconsumed messages by all consumer groups across all partitions of the current topic. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
topic consumegroup consume speed | Count/min | Total consumption rate of all consumer groups across all partitions of the current topic. It is summed according to the selected time granularity. |
Consumer group - Partition monitoringConsumer group - Partition monitoring
Metric Name | Unit | Description |
partition consumegroup consume speed | Count/min | Consumption rate of the consumer group in the current partition (messages per minute). |
partition consumegroup message consume offset | / | Current consumption offset of the consumer group in the current partition. |
partition max offset | / | Maximum offset of the current partition. |
partition consumegroup unconsume message count | Count | Number of unconsumed messages by the consumer group in the current partition. |
For more information about the Chinese-English comparison of monitoring metrics, see For more information about the Chinese-English comparison of monitoring metrics, see CKafka Monitoring MetricsCKafka Monitoring Metrics..
For more information about monitoring-related APIs, see the following documents: For more information about monitoring-related APIs, see the following documents: Topic MonitoringTopic Monitoring, , Instance MonitoringInstance Monitoring, and , and Consumer Group MonitoringConsumer Group Monitoring..
Advanced Metric (Pro Edition)Advanced Metric (Pro Edition)
In addition to the basic monitoring metrics, CKafka Pro Edition clusters support the advanced monitoring capability. Through advanced monitoring, you can view node-level monitoring metrics, which are used for business troubleshooting scenarios such as exception detection, traffic throttling analysis, and duration analysis. The following tables introduce and describe all monitoring metrics provided by the advanced monitoring capability of CKafka.In addition to the basic monitoring metrics, CKafka Pro Edition clusters support the advanced monitoring capability. Through advanced monitoring, you can view node-level monitoring metrics, which are used for business troubleshooting scenarios such as exception detection, traffic throttling analysis, and duration analysis. The following tables introduce and describe all monitoring metrics provided by the advanced monitoring capability of CKafka.
Monitoring MetricMonitoring Metric | Metric DescriptionMetric Description | Normal Value RangeNormal Value Range | Handling RecommendationHandling Recommendation |
Live Broker NodesLive Broker Nodes | The service status of each broker node. This metric allows you to monitor node availability through the heartbeat mechanism.The service status of each broker node. This metric allows you to monitor node availability through the heartbeat mechanism. | The normal value is 100%.The normal value is 100%. If the node liveness rate is below the normal value, namely, a broker is down, it will trigger in-sync replica (ISR) shrinking.If the node liveness rate is below the normal value, namely, a broker is down, it will trigger in-sync replica (ISR) shrinking. | When the node status is abnormal, it is recommended to immediately restart the faulty node and check the system resource usage.When the node status is abnormal, it is recommended to immediately restart the faulty node and check the system resource usage. If multiple restart attempts fail, contact If multiple restart attempts fail, contact online customer serviceonline customer service.. |
Cluster LoadCluster Load | Cluster overall load, which is the maximum value among all nodes.Cluster overall load, which is the maximum value among all nodes. | Single-AZ deployment: Cluster load < 70%.Single-AZ deployment: Cluster load < 70%. Two-AZ deployment: Normal cluster load < 35%.Two-AZ deployment: Normal cluster load < 35%. Three-AZ deployment: Normal cluster load < 47%.Three-AZ deployment: Normal cluster load < 47%. If the bandwidth utilization is low but the cluster load is high, it is necessary to scale out the cluster bandwidth based on cluster load metrics.If the bandwidth utilization is low but the cluster load is high, it is necessary to scale out the cluster bandwidth based on cluster load metrics. | It is recommended to promptly upgrade the cluster bandwidth specification when the load is excessively high. For more information, see It is recommended to promptly upgrade the cluster bandwidth specification when the load is excessively high. For more information, see Use Cases of Cluster Capacity PlanningUse Cases of Cluster Capacity Planning.. |
Monitoring MetricMonitoring Metric | Metric DescriptionMetric Description | Normal Value RangeNormal Value Range | Handling RecommendationHandling Recommendation |
Network Idle DegreeNetwork Idle Degree | Used to measure the remaining I/O resources for concurrent network processing on an instance. A value closer to 1 indicates more idle resources.Used to measure the remaining I/O resources for concurrent network processing on an instance. A value closer to 1 indicates more idle resources. | This value generally fluctuates from 0.5 to 1. A value less than 0.3 indicates a high load.This value generally fluctuates from 0.5 to 1. A value less than 0.3 indicates a high load. | If this value remains below 0.3, check the instance bandwidth utilization and disk usage percentage on the monitoring page in the console.If this value remains below 0.3, check the instance bandwidth utilization and disk usage percentage on the monitoring page in the console. If the bandwidth exceeds 80%, upgrade the specifications to scale up. If the disk usage percentage exceeds 80%, adjust disk capacity or enable the disk watermark adjustment policy.If the bandwidth exceeds 80%, upgrade the specifications to scale up. If the disk usage percentage exceeds 80%, adjust disk capacity or enable the disk watermark adjustment policy. For scaling operations, see For scaling operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications. To enable the disk watermark adjustment policy, see . To enable the disk watermark adjustment policy, see Configuring the Disk Watermark Adjustment PolicyConfiguring the Disk Watermark Adjustment Policy.. |
Request Queue DepthRequest Queue Depth | It reflects the number of unprocessed production requests. A large value may indicate excessive concurrent requests, high CPU load, or a disk I/O bottleneck.It reflects the number of unprocessed production requests. A large value may indicate excessive concurrent requests, high CPU load, or a disk I/O bottleneck. | If the value consistently equals 2000, it indicates that the cluster load is relatively high.If the value consistently equals 2000, it indicates that the cluster load is relatively high. Values less than 2000 can be ignored. No impact is expected.Values less than 2000 can be ignored. No impact is expected. | If clients experience production/consumption timeouts but the Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM) instance load is normal, it indicates the request queue of a single CVM instance has reached its upper limit. The request queue length for a single-node broker is set to 500 by default. You can If clients experience production/consumption timeouts but the Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM) instance load is normal, it indicates the request queue of a single CVM instance has reached its upper limit. The request queue length for a single-node broker is set to 500 by default. You can submit a ticketsubmit a ticket to have it adjusted appropriately based on purchased resources. to have it adjusted appropriately based on purchased resources. |
Unsynced ReplicasUnsynced Replicas | Number of OSRs in a cluster. If an instance has OSRs, the cluster may have potential health issues.Number of OSRs in a cluster. If an instance has OSRs, the cluster may have potential health issues. | To ensure your instance runs normally, CKafka sets up certain built-in topics. These topics may be offline under certain circumstances, but are counted in the number of OSRs, which does not affect your business operations.To ensure your instance runs normally, CKafka sets up certain built-in topics. These topics may be offline under certain circumstances, but are counted in the number of OSRs, which does not affect your business operations. Under normal circumstances, the number of OSRs should be below 5. If the value remains above 5 for an extended period, it indicates that intervention is required.Under normal circumstances, the number of OSRs should be below 5. If the value remains above 5 for an extended period, it indicates that intervention is required. Occasional broker fluctuations, where the curve value spikes and then returns to normal after a period, are normal phenomena.Occasional broker fluctuations, where the curve value spikes and then returns to normal after a period, are normal phenomena. | When the curve value remains above 5 for an extended period, it indicates that the cluster has OSRs. This is usually caused by broker node exceptions or network issues. Check the broker logs for troubleshooting.When the curve value remains above 5 for an extended period, it indicates that the cluster has OSRs. This is usually caused by broker node exceptions or network issues. Check the broker logs for troubleshooting. |
ZK ReconnectionsZK Reconnections | The number of times the persistent connection between the broker and ZooKeeper disconnects and reconnects. Network fluctuations or high cluster load may cause disconnections and reconnections, which can trigger a The number of times the persistent connection between the broker and ZooKeeper disconnects and reconnects. Network fluctuations or high cluster load may cause disconnections and reconnections, which can trigger a leader switchleader switch when they occur. when they occur. | There is no normal value range. This value is cumulative. It increments by 1 after each disconnection since broker startup and is reset to 0 only when the broker restarts.There is no normal value range. This value is cumulative. It increments by 1 after each disconnection since broker startup and is reset to 0 only when the broker restarts. The number of ZooKeeper disconnections is cumulative. A high value does not necessarily indicate a cluster issue. Monitor the frequency of ZooKeeper disconnections. If they occur frequently, further troubleshooting is required.The number of ZooKeeper disconnections is cumulative. A high value does not necessarily indicate a cluster issue. Monitor the frequency of ZooKeeper disconnections. If they occur frequently, further troubleshooting is required. | Check in the console whether the cluster load exceeds 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, you can upgrade the bandwidth specifications of the cluster. For specific operations, see Check in the console whether the cluster load exceeds 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, you can upgrade the bandwidth specifications of the cluster. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
ISR ExpansionsISR Expansions | ISR refers to the set of follower replicas that remain synchronized with the leader replica. The metric value increases by 1 when an OSR catches up with the leader's data and rejoins the ISR.ISR refers to the set of follower replicas that remain synchronized with the leader replica. The metric value increases by 1 when an OSR catches up with the leader's data and rejoins the ISR. | There is no normal value range. Expansions may occur when the cluster experiences fluctuations.There is no normal value range. Expansions may occur when the cluster experiences fluctuations. Infrequent fluctuations (for example, less than 3 times per hour) require no intervention. If the value persistently increases, troubleshooting is required.Infrequent fluctuations (for example, less than 3 times per hour) require no intervention. If the value persistently increases, troubleshooting is required. | It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level is normal, clients can optimize producer parameters by setting linger.ms to a non-zero value and ack to 1. This ensures throughput while reducing synchronization pressure on the cluster.If the cluster load level is normal, clients can optimize producer parameters by setting linger.ms to a non-zero value and ack to 1. This ensures throughput while reducing synchronization pressure on the cluster. If ISR issues frequently occur, affecting production or consumption, and the situation does not recover for an extended period, If ISR issues frequently occur, affecting production or consumption, and the situation does not recover for an extended period, contact uscontact us.. |
ISR ShrinksISR Shrinks | Number of Kafka ISR shrinkings. An ISR shrinking occurs when a broker goes down or when ZooKeeper reconnection happens.Number of Kafka ISR shrinkings. An ISR shrinking occurs when a broker goes down or when ZooKeeper reconnection happens. | There is no normal value range. Shrinkings may occur when the cluster experiences fluctuations.There is no normal value range. Shrinkings may occur when the cluster experiences fluctuations. Instantaneous fluctuations have no impact. If they occur frequently over an extended period, a check is required.Instantaneous fluctuations have no impact. If they occur frequently over an extended period, a check is required. | It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications.It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. If the cluster load level is normal, it is recommended to perform manual partition balancing for high-load partitions.If the cluster load level is normal, it is recommended to perform manual partition balancing for high-load partitions. For messages with keys, ensure balanced writes by setting a partition policy.For messages with keys, ensure balanced writes by setting a partition policy. If a single partition becomes a bottleneck, increase the number of partitions to improve write parallelism.If a single partition becomes a bottleneck, increase the number of partitions to improve write parallelism. |
Instance Broker Storage UtilizationInstance Broker Storage Utilization | Disk utilization of each broker in a cluster. The maximum value is taken over the unit time period.Disk utilization of each broker in a cluster. The maximum value is taken over the unit time period. | This value generally ranges from 0% to 100%.This value generally ranges from 0% to 100%. If the value exceeds 80%, relevant measures need to be taken.If the value exceeds 80%, relevant measures need to be taken. | Upgrade the storage specifications. It is recommended to reserve 30% disk buffer space.Upgrade the storage specifications. It is recommended to reserve 30% disk buffer space. |
Monitoring MetricMonitoring Metric | Metric DescriptionMetric Description | Normal Value RangeNormal Value Range | Handling RecommendationHandling Recommendation |
Broker Node Production Throttling OccurrencesBroker Node Production Throttling Occurrences | Number of production traffic throttling events triggered on each broker node.Number of production traffic throttling events triggered on each broker node. | There is no normal value range.There is no normal value range. Occasional bursts of traffic throttling are normal and have no impact on business operations, requiring no special attention. If traffic throttling occurs persistently and frequently, further troubleshooting is required.Occasional bursts of traffic throttling are normal and have no impact on business operations, requiring no special attention. If traffic throttling occurs persistently and frequently, further troubleshooting is required. | Check the bandwidth utilization. If the production traffic exceeds 80% of the bandwidth specifications, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Check the bandwidth utilization. If the production traffic exceeds 80% of the bandwidth specifications, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. Ensure that the number of partitions is an integer multiple of the number of nodes, preventing write bottlenecks in any single partition. If bottlenecks occur, adjust the partition policy to ensure balanced write distribution.Ensure that the number of partitions is an integer multiple of the number of nodes, preventing write bottlenecks in any single partition. If bottlenecks occur, adjust the partition policy to ensure balanced write distribution. Enable the automatic disk capacity expansion feature in the disk watermark adjustment policy. For specific operations, see Enable the automatic disk capacity expansion feature in the disk watermark adjustment policy. For specific operations, see Configuring the Disk Watermark Adjustment PolicyConfiguring the Disk Watermark Adjustment Policy.. |
Production traffic of Broker node(MB)Production traffic of Broker node(MB) | Production traffic of each broker node.Production traffic of each broker node. | There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications.There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications. No special attention is needed if the production traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased bandwidth specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required.No special attention is needed if the production traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased bandwidth specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required. | It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If a single node consistently experiences high load, it is necessary to determine whether there is a write imbalance, for example, when messages are configured with keys, and optimize the write imbalance issue.If a single node consistently experiences high load, it is necessary to determine whether there is a write imbalance, for example, when messages are configured with keys, and optimize the write imbalance issue. |
Maximum production rate/sec (Bytes/s)Maximum production rate/sec (Bytes/s) | Maximum production traffic of each broker node.Maximum production traffic of each broker node. | There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications.There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications. No special attention is needed if the peak value of maximum production traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required.No special attention is needed if the peak value of maximum production traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required. | It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If a single node consistently experiences high load, manual partition balancing is required.If a single node consistently experiences high load, manual partition balancing is required. |
Production Traffic Usage Rate by Broker (%)Production Traffic Usage Rate by Broker (%) | Percentage of production traffic generated by a single-node broker relative to the purchased traffic.Percentage of production traffic generated by a single-node broker relative to the purchased traffic. | This value generally ranges from 0% to 100%.This value generally ranges from 0% to 100%. Short-term peaks in utilization may be normal business activity and require no special attention. If the utilization remains consistently high, further action is recommended.Short-term peaks in utilization may be normal business activity and require no special attention. If the utilization remains consistently high, further action is recommended. | If this value consistently exceeds 80%, it is recommended to upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see If this value consistently exceeds 80%, it is recommended to upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Total Production DurationTotal Production Duration | Total duration of production requests, aggregated from the following metrics: response queue duration, delayed response duration, fetch request duration, local processing duration, and request queue duration.Total duration of production requests, aggregated from the following metrics: response queue duration, delayed response duration, fetch request duration, local processing duration, and request queue duration. At each point in time, the total duration does not equal the sum of the above five durations because each metric is averaged independently.At each point in time, the total duration does not equal the sum of the above five durations because each metric is averaged independently. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 100 ms. A duration of 0 to 1000 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 100 ms. A duration of 0 to 1000 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 1000 ms.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 1000 ms. If it consistently exceeds 1000 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 1000 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level is normal, try optimizing producer parameters by setting ack to -1 and changing linger.ms to a non-zero value for write optimization.If the cluster load level is normal, try optimizing producer parameters by setting ack to -1 and changing linger.ms to a non-zero value for write optimization. |
Request queue durationRequest queue duration | Period of time during which production requests wait in the request receiving queue, indicating the time request packets wait for subsequent processing.Period of time during which production requests wait in the request receiving queue, indicating the time request packets wait for subsequent processing. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms. If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level is normal, try optimizing producer parameters by setting ack to -1 and changing linger.ms to a non-zero value for write optimization.If the cluster load level is normal, try optimizing producer parameters by setting ack to -1 and changing linger.ms to a non-zero value for write optimization. |
Local processing durationLocal processing duration | Period of time during which production requests are processed on the leader broker, namely, the duration from taking the request packet from the request queue to writing it to the local page cache.Period of time during which production requests are processed on the leader broker, namely, the duration from taking the request packet from the request queue to writing it to the local page cache. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms. If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | It is recommended to use clusters with SSD disk storage.It is recommended to use clusters with SSD disk storage. In batch write scenarios, it is recommended to increase batch.size and linger.ms to improve the batch forming efficiency.In batch write scenarios, it is recommended to increase batch.size and linger.ms to improve the batch forming efficiency. |
Acknowledgment wait durationAcknowledgment wait duration | Period of time during which production requests wait for data synchronization. This value is greater than 0 only when ack of the client is set to -1. It remains 0 when ack is set to 1 or 0.Period of time during which production requests wait for data synchronization. This value is greater than 0 only when ack of the client is set to -1. It remains 0 when ack is set to 1 or 0. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 200 ms. A duration of 0 to 500 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 200 ms. A duration of 0 to 500 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. For cross-AZ instances with ack set to -1, this value is higher than that for non-cross-AZ instances. For more information, see For cross-AZ instances with ack set to -1, this value is higher than that for non-cross-AZ instances. For more information, see High Reliability of ClustersHigh Reliability of Clusters.. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 500 ms. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 500 ms. If it consistently exceeds 500 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 500 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | Reduce the number of replicas (setting ack to 1 prioritizes production and throughput protection).Reduce the number of replicas (setting ack to 1 prioritizes production and throughput protection). |
Delayed response durationDelayed response duration | Period of time during which the system delays production requests before returning a response. This value is 0 when the instance traffic does not exceed the purchased traffic, and becomes greater than 0 if traffic is throttled.Period of time during which the system delays production requests before returning a response. This value is 0 when the instance traffic does not exceed the purchased traffic, and becomes greater than 0 if traffic is throttled. | If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time.If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time. If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes.If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes. | When the value consistently exceeds 0, initiate traffic throttling on the producer and check the source of burst traffic.When the value consistently exceeds 0, initiate traffic throttling on the producer and check the source of burst traffic. If the threshold is consistently exceeded, upgrade the specifications to scale up the bandwidth. For specific operations, see If the threshold is consistently exceeded, upgrade the specifications to scale up the bandwidth. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Response queue durationResponse queue duration | Period of time during which production requests wait in the response queue, indicating the time request packets wait to be sent to the client.Period of time during which production requests wait in the response queue, indicating the time request packets wait to be sent to the client. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms. If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | Check network congestion and the number of TCP connections, optimize connection reuse on the producer, and reduce the load on the node where the producer resides.Check network congestion and the number of TCP connections, optimize connection reuse on the producer, and reduce the load on the node where the producer resides. |
Production Response Duration (95th)Production Response Duration (95th) | 95% of production requests have a delayed response duration lower than this value.95% of production requests have a delayed response duration lower than this value. | If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time.If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time. If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes.If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes. | This scenario generally occurs during traffic throttling. Check whether the bandwidth is exceeded and the extent of the exceedance.This scenario generally occurs during traffic throttling. Check whether the bandwidth is exceeded and the extent of the exceedance. If the metric value consistently exceeds the threshold, action is required. You can resolve the issue by upgrading the specifications. For specific operations, see If the metric value consistently exceeds the threshold, action is required. You can resolve the issue by upgrading the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Monitoring MetricMonitoring Metric | Metric DescriptionMetric Description | Normal Value RangeNormal Value Range | Handling RecommendationHandling Recommendation |
Broker Node Consumption Throttling OccurrencesBroker Node Consumption Throttling Occurrences | Number of consumption traffic throttling events triggered on each broker node.Number of consumption traffic throttling events triggered on each broker node. | There is no normal value range.There is no normal value range. Occasional bursts of traffic throttling are normal and have no impact on business operations, requiring no special attention. If traffic throttling occurs persistently and frequently, further troubleshooting is required.Occasional bursts of traffic throttling are normal and have no impact on business operations, requiring no special attention. If traffic throttling occurs persistently and frequently, further troubleshooting is required. | Check the bandwidth utilization. If the consumption traffic exceeds 80% of the bandwidth specifications, scale up the bandwidth. For scaling operations, see Check the bandwidth utilization. If the consumption traffic exceeds 80% of the bandwidth specifications, scale up the bandwidth. For scaling operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. Enable the automatic disk capacity expansion feature in the disk watermark adjustment policy. For specific operations, see Enable the automatic disk capacity expansion feature in the disk watermark adjustment policy. For specific operations, see Configuring the Disk Watermark Adjustment PolicyConfiguring the Disk Watermark Adjustment Policy.. |
Consumption traffic of Broker node(MB)Consumption traffic of Broker node(MB) | Consumption traffic of each broker node.Consumption traffic of each broker node. | There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications.There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications. No special attention is needed if the consumption traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased bandwidth specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required.No special attention is needed if the consumption traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased bandwidth specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required. | It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. Enable the elastic bandwidth capability. For specific operations, see Enable the elastic bandwidth capability. For specific operations, see Enabling Elastic BandwidthEnabling Elastic Bandwidth.. |
Maximum consumption traffic/sec (bytes/s)Maximum consumption traffic/sec (bytes/s) | Maximum consumption traffic of each broker node.Maximum consumption traffic of each broker node. | There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications.There is no normal value range, as it fluctuates based on business activities and purchased specifications. No special attention is needed if the peak value of maximum consumption traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required.No special attention is needed if the peak value of maximum consumption traffic occasionally exceeds the purchased specifications. If it consistently exceeds the purchased specifications, further action is required. | It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see It is recommended to upgrade the bandwidth specifications and reserve at least a 20% buffer. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. Enable the elastic bandwidth capability. For specific operations, see Enable the elastic bandwidth capability. For specific operations, see Enabling Elastic BandwidthEnabling Elastic Bandwidth.. |
Consumption Traffic Usage Rate by BrokerConsumption Traffic Usage Rate by Broker | Percentage of consumption traffic generated by a single-node broker relative to the purchased traffic.Percentage of consumption traffic generated by a single-node broker relative to the purchased traffic. | This value generally ranges from 0% to 100%.This value generally ranges from 0% to 100%. If this value consistently exceeds 80%, consider upgrading the specifications.If this value consistently exceeds 80%, consider upgrading the specifications. | If this value consistently exceeds 80%, it is recommended to upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see If this value consistently exceeds 80%, it is recommended to upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Total Consumption DurationTotal Consumption Duration | Total duration of consumption requests, aggregated from the following metrics: response queue duration, delayed response duration, fetch request duration, local processing duration, and request queue duration.Total duration of consumption requests, aggregated from the following metrics: response queue duration, delayed response duration, fetch request duration, local processing duration, and request queue duration. At each point in time, the total duration does not equal the sum of the above five durations because each metric is averaged independently.At each point in time, the total duration does not equal the sum of the above five durations because each metric is averaged independently. | Generally, the value ranges from 500 ms to 1000 ms (the default value of the fetch.max.wait.ms parameter for the client is 500 ms). A duration of 500 to 5000 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 500 ms to 1000 ms (the default value of the fetch.max.wait.ms parameter for the client is 500 ms). A duration of 500 to 5000 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. If it consistently exceeds 5000 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 5000 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. Increase the consumer timeout parameter request.timeout.ms to avoid false timeout detection.Increase the consumer timeout parameter request.timeout.ms to avoid false timeout detection. |
Request queue durationRequest queue duration | Period of time during which consumption requests wait in the request queue, indicating the time request packets wait for subsequent processing.Period of time during which consumption requests wait in the request queue, indicating the time request packets wait for subsequent processing. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms. If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see It is recommended to maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level is normal, try optimizing producer parameters by setting ack to -1 and changing linger.ms to a non-zero value for write optimization.If the cluster load level is normal, try optimizing producer parameters by setting ack to -1 and changing linger.ms to a non-zero value for write optimization. |
Local processing durationLocal processing duration | Period of time during which consumption requests pull data on the leader broker, namely, reading data from the local disk.Period of time during which consumption requests pull data on the leader broker, namely, reading data from the local disk. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 500 ms. A duration of 0 to 1000 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 500 ms. A duration of 0 to 1000 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 1000 ms, as consumption may involve reading cold data, which can result in an extended duration.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 1000 ms, as consumption may involve reading cold data, which can result in an extended duration. If it consistently exceeds 1000 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 1000 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | It is recommended to use clusters with SSD disk storage.It is recommended to use clusters with SSD disk storage. |
Consumption wait durationConsumption wait duration | The default value of the fetch.max.wait.ms parameter for the client is 500 ms. This value indicates how long the server is allowed to wait before returning a response to the client when no data is available.The default value of the fetch.max.wait.ms parameter for the client is 500 ms. This value indicates how long the server is allowed to wait before returning a response to the client when no data is available. | Generally, the value is around 500 ms (the default value of the fetch.max.wait.ms parameter for the client is 500 ms). The value depends on the parameter settings of the client.Generally, the value is around 500 ms (the default value of the fetch.max.wait.ms parameter for the client is 500 ms). The value depends on the parameter settings of the client. | Adjust the wait interval fetch.max.wait.ms based on your business requirements.Adjust the wait interval fetch.max.wait.ms based on your business requirements. Note:Note: In scenarios where consumption is stopped, the fetch duration should not be used as a reference for evaluating the latency. Instead, multiple metrics such as health status, consumption latency, and consumption backlogs should be considered together.In scenarios where consumption is stopped, the fetch duration should not be used as a reference for evaluating the latency. Instead, multiple metrics such as health status, consumption latency, and consumption backlogs should be considered together. |
Delayed response durationDelayed response duration | Period of time during which the system delays consumption requests before returning a response. This value is 0 when the instance traffic does not exceed the purchased traffic, and becomes greater than 0 if traffic is throttled.Period of time during which the system delays consumption requests before returning a response. This value is 0 when the instance traffic does not exceed the purchased traffic, and becomes greater than 0 if traffic is throttled. | If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time.If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time. If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes.If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes. | When the value consistently exceeds 0, initiate traffic throttling on the consumer and check the source of burst traffic.When the value consistently exceeds 0, initiate traffic throttling on the consumer and check the source of burst traffic. If the threshold is consistently exceeded, upgrade the specifications to scale up the bandwidth. For specific operations, see If the threshold is consistently exceeded, upgrade the specifications to scale up the bandwidth. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Response queue durationResponse queue duration | Period of time during which consumption requests wait in the response queue, indicating the time request packets wait to be sent to the client.Period of time during which consumption requests wait in the response queue, indicating the time request packets wait to be sent to the client. | Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume.Generally, the value ranges from 0 ms to 50 ms. A duration of 0 ms to 200 ms is normal during periods of high data volume. No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms.No action is needed if the value is not consistently above 200 ms. If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended.If it consistently exceeds 200 ms, further troubleshooting is recommended. | Optimize the network configuration of the consumer and reduce the wait interval fetch.max.wait.ms.Optimize the network configuration of the consumer and reduce the wait interval fetch.max.wait.ms. Check the TCP retransmission rate of broker nodes.Check the TCP retransmission rate of broker nodes. If the load on the node where the consumer resides is high, upgrade the specifications or perform scale-out. For specific operations, see If the load on the node where the consumer resides is high, upgrade the specifications or perform scale-out. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Consumption Response Duration (95th)Consumption Response Duration (95th) | 95% of consumption requests have a delayed response duration lower than this value.95% of consumption requests have a delayed response duration lower than this value. | If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time.If the instance does not exceed the threshold, this value remains 0 over time. If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes.If the instance exceeds the threshold, it will be delayed by 0 to 5 minutes based on the extent of the exceedance, meaning the maximum value is 5 minutes. | This scenario generally occurs during traffic throttling. Confirm whether the bandwidth specifications are exceeded.This scenario generally occurs during traffic throttling. Confirm whether the bandwidth specifications are exceeded. If the metric value consistently exceeds the threshold, action is required. You can resolve the issue by upgrading the specifications. For specific operations, see If the metric value consistently exceeds the threshold, action is required. You can resolve the issue by upgrading the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Monitoring MetricMonitoring Metric | Metric DescriptionMetric Description | Normal Value RangeNormal Value Range | Handling RecommendationHandling Recommendation |
CpuUsage(%)CpuUsage(%) | CPU utilization is the percentage of total CPU time occupied by a process over a period.CPU utilization is the percentage of total CPU time occupied by a process over a period. | This value generally ranges from 1% to 100%.This value generally ranges from 1% to 100%. If the value consistently exceeds 90% for more than 5 consecutive cycles, it indicates a very high system load, requiring troubleshooting.If the value consistently exceeds 90% for more than 5 consecutive cycles, it indicates a very high system load, requiring troubleshooting. | Upgrade the instance specifications. For specific operations, see Upgrade the instance specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
LanIntraffic (MB)LanIntraffic (MB) | Private network inbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM) instance for communication within a cluster. The actual limits for private network bandwidth and packet receiving capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications.Private network inbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM) instance for communication within a cluster. The actual limits for private network bandwidth and packet receiving capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications. | This value is generally greater than 0 (data will be generated from CVM instance monitoring within the cluster).This value is generally greater than 0 (data will be generated from CVM instance monitoring within the cluster). If no inbound bandwidth is generated, it indicates a CVM service exception or network unreachability.If no inbound bandwidth is generated, it indicates a CVM service exception or network unreachability. | Check security group rules.Check security group rules. Troubleshoot Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network routing issues. If there is data but the specification limit is exceeded, purchase a private network bandwidth package.Troubleshoot Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network routing issues. If there is data but the specification limit is exceeded, purchase a private network bandwidth package. |
LanOuttraffic(MB)LanOuttraffic(MB) | Private network outbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a CVM instance for communication within a cluster. The actual limits for private network bandwidth and packet sending capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications.Private network outbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a CVM instance for communication within a cluster. The actual limits for private network bandwidth and packet sending capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications. | This value is generally greater than 0 (data will be generated from CVM instance monitoring within the cluster).This value is generally greater than 0 (data will be generated from CVM instance monitoring within the cluster). If no outbound bandwidth is generated, it indicates a CVM service exception or network unreachability.If no outbound bandwidth is generated, it indicates a CVM service exception or network unreachability. | Check security group rules.Check security group rules. Troubleshoot VPC network routing issues. If there is data but the specification limit is exceeded, purchase a private network bandwidth package.Troubleshoot VPC network routing issues. If there is data but the specification limit is exceeded, purchase a private network bandwidth package. |
MemUsage(%)MemUsage(%) | Memory utilization is the percentage of the total memory space occupied, calculated as the total memory space minus all available memory space.Memory utilization is the percentage of the total memory space occupied, calculated as the total memory space minus all available memory space. | The normal value range is from 1% to 100%.The normal value range is from 1% to 100%. If the memory utilization reaches or exceeds 90%, it indicates that programs are occupying excessive memory, requiring intervention on certain processes.If the memory utilization reaches or exceeds 90%, it indicates that programs are occupying excessive memory, requiring intervention on certain processes. | Upgrade the bandwidth specifications to increase physical resources. For specific operations, see Upgrade the bandwidth specifications to increase physical resources. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. |
Intraffic (Bit/s)Intraffic (Bit/s) | Public network inbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a CVM instance for communication over the public network. The actual limits for public network bandwidth and packet receiving capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications.Public network inbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a CVM instance for communication over the public network. The actual limits for public network bandwidth and packet receiving capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications. | The value is greater than 0 when inbound traffic is generated over the public network. Otherwise, it is 0.The value is greater than 0 when inbound traffic is generated over the public network. Otherwise, it is 0. If it is abnormally 0, further troubleshooting is required.If it is abnormally 0, further troubleshooting is required. | Check whether you have overdue payments for the Elastic IP (EIP) service.Check whether you have overdue payments for the Elastic IP (EIP) service. If the specification limit is exceeded, upgrade the public network bandwidth. For specific operations, see If the specification limit is exceeded, upgrade the public network bandwidth. For specific operations, see Configuring Public Network AccessConfiguring Public Network Access.. |
Outtraffic(Bit/s)Outtraffic(Bit/s) | Public network outbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a CVM instance for communication over the public network. The actual limits for public network bandwidth and packet sending capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications.Public network outbound bandwidth refers to the bandwidth achievable by a CVM instance for communication over the public network. The actual limits for public network bandwidth and packet sending capability are determined by the purchased instance specifications. | The value is greater than 0 when outbound traffic is generated over the public network. Otherwise, it is 0.The value is greater than 0 when outbound traffic is generated over the public network. Otherwise, it is 0. If it is abnormally 0, further troubleshooting is required.If it is abnormally 0, further troubleshooting is required. | Check whether you have overdue payments for the Elastic IP (EIP) service.Check whether you have overdue payments for the Elastic IP (EIP) service. If the specification limit is exceeded, upgrade the public network bandwidth. For specific operations, see If the specification limit is exceeded, upgrade the public network bandwidth. For specific operations, see Configuring Public Network AccessConfiguring Public Network Access.. |
Monitoring MetricMonitoring Metric | Metric DescriptionMetric Description | Normal Value RangeNormal Value Range | Handling RecommendationHandling Recommendation |
HeapUsage(%)HeapUsage(%) | Percentage of JVM heap memory used by the broker relative to the total heap memory. The maximum value is taken over the unit time period.Percentage of JVM heap memory used by the broker relative to the total heap memory. The maximum value is taken over the unit time period. | The maximum value of this metric typically fluctuates from 80% to 90%.The maximum value of this metric typically fluctuates from 80% to 90%. If the value shows a persistent upward trend over an extended period, pay attention to the usage pattern of heap memory.If the value shows a persistent upward trend over an extended period, pay attention to the usage pattern of heap memory. | Maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level does not exceed the threshold, ensure you are using the latest version. If not, upgrade the cluster to the latest version. For specific operations, see If the cluster load level does not exceed the threshold, ensure you are using the latest version. If not, upgrade the cluster to the latest version. For specific operations, see Upgrading the Kernel Minor Version of InstancesUpgrading the Kernel Minor Version of Instances.. If you are using the latest version and the issue persists, contact If you are using the latest version and the issue persists, contact online customer serviceonline customer service.. |
LastYoungGcCountLastYoungGcCount | Number of young garbage collection (GC) events for the broker.Number of young garbage collection (GC) events for the broker. | The normal value range is from 0 to 300.The normal value range is from 0 to 300. If the value consistently exceeds 300, adjust the GC parameters.If the value consistently exceeds 300, adjust the GC parameters. | Maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level does not exceed the threshold, ensure you are using the latest version. If not, upgrade the cluster to the latest version. For specific operations, see If the cluster load level does not exceed the threshold, ensure you are using the latest version. If not, upgrade the cluster to the latest version. For specific operations, see Upgrading the Kernel Minor Version of InstancesUpgrading the Kernel Minor Version of Instances.. If you are using the latest version and the issue persists, contact If you are using the latest version and the issue persists, contact online customer serviceonline customer service.. |
LastOldGcCountLastOldGcCount | Number of full GC events for the broker.Number of full GC events for the broker. | The normal value is 0.The normal value is 0. If the value becomes greater than 0, intervention is required.If the value becomes greater than 0, intervention is required. | Maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Maintain the cluster load level below 80%. If the threshold is exceeded, upgrade the specifications. For specific operations, see Changing Instance SpecificationsChanging Instance Specifications.. If the cluster load level does not exceed the threshold, ensure you are using the latest version. If not, upgrade the cluster to the latest version. For specific operations, see If the cluster load level does not exceed the threshold, ensure you are using the latest version. If not, upgrade the cluster to the latest version. For specific operations, see Upgrading the Kernel Minor Version of InstancesUpgrading the Kernel Minor Version of Instances.. If you are using the latest version and the issue persists, contact If you are using the latest version and the issue persists, contact online customer serviceonline customer service.. |
Dashboard Metrics (Pro Edition)Dashboard Metrics (Pro Edition)
CKafka Pro Edition clusters support the dashboard capability, which displays top rankings of key metrics to assist in business optimization analysis scenarios such as production/consumption hotspot analysis and disk usage analysis.CKafka Pro Edition clusters support the dashboard capability, which displays top rankings of key metrics to assist in business optimization analysis scenarios such as production/consumption hotspot analysis and disk usage analysis.
This metric shows the total number of TCP connections on a broker. You can use the drop-down list to switch and view the number of TCP connections on different brokers. When the number of TCP connections is less than or equal to 500, the system supports full data download.This metric shows the total number of TCP connections on a broker. You can use the drop-down list to switch and view the number of TCP connections on different brokers. When the number of TCP connections is less than or equal to 500, the system supports full data download.
You can quickly check the connections of each machine. If the number of connections is close to or reaches the upper limit, it is recommended to prioritize troubleshooting abnormal connections or scaling out the instance to avoid affecting service availability.You can quickly check the connections of each machine. If the number of connections is close to or reaches the upper limit, it is recommended to prioritize troubleshooting abnormal connections or scaling out the instance to avoid affecting service availability.
Details of unsynced replicas: displays out-of-sync replica (OSR) details for a specified topic. This metric can be used to quickly locate partitions with replica synchronization exceptions, ensuring data redundancy and availability.Details of unsynced replicas: displays out-of-sync replica (OSR) details for a specified topic. This metric can be used to quickly locate partitions with replica synchronization exceptions, ensuring data redundancy and availability.
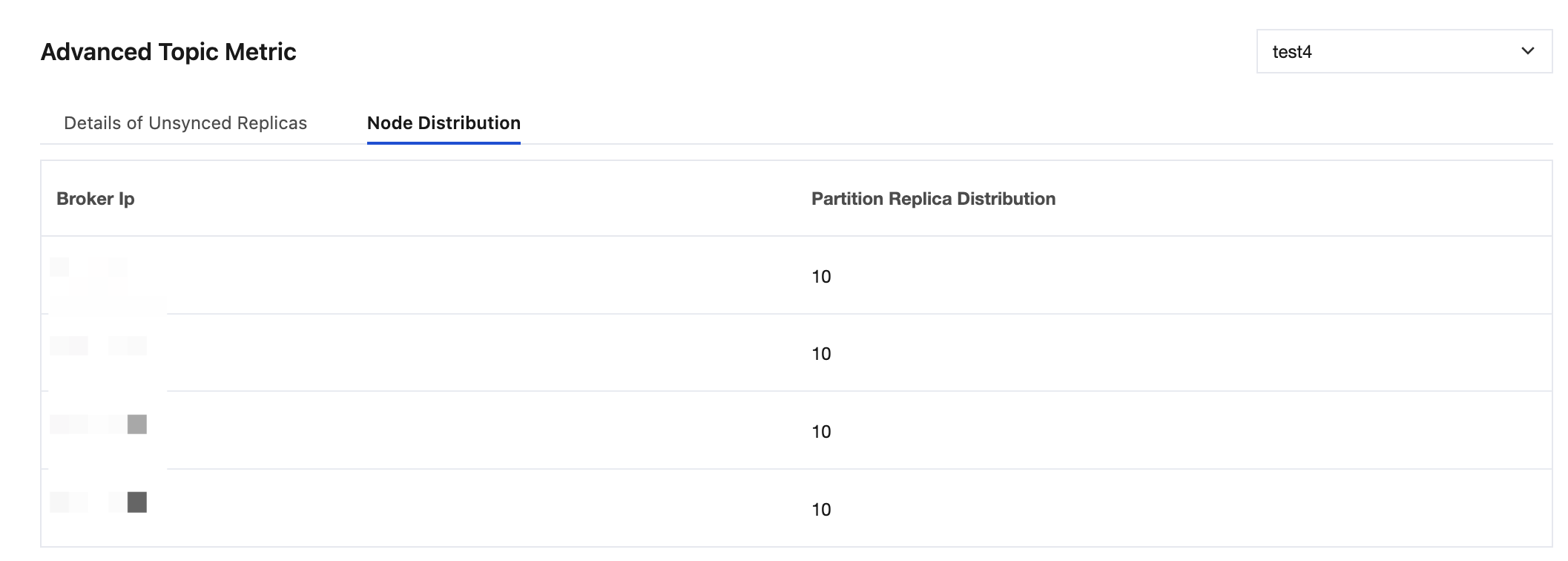
Node Distribution: displays the distribution of replicas for a specified topic across broker nodes. This metric can be used in the following scenarios:Node Distribution: displays the distribution of replicas for a specified topic across broker nodes. This metric can be used in the following scenarios:
It helps locate brokers with uneven replica distribution.It helps locate brokers with uneven replica distribution.
It is used for disaster recovery assessment, ensuring partition replicas are distributed across different nodes.It is used for disaster recovery assessment, ensuring partition replicas are distributed across different nodes.
It provides data migration reference for cluster scaling and helps with the planning of node addition or removal.It provides data migration reference for cluster scaling and helps with the planning of node addition or removal.
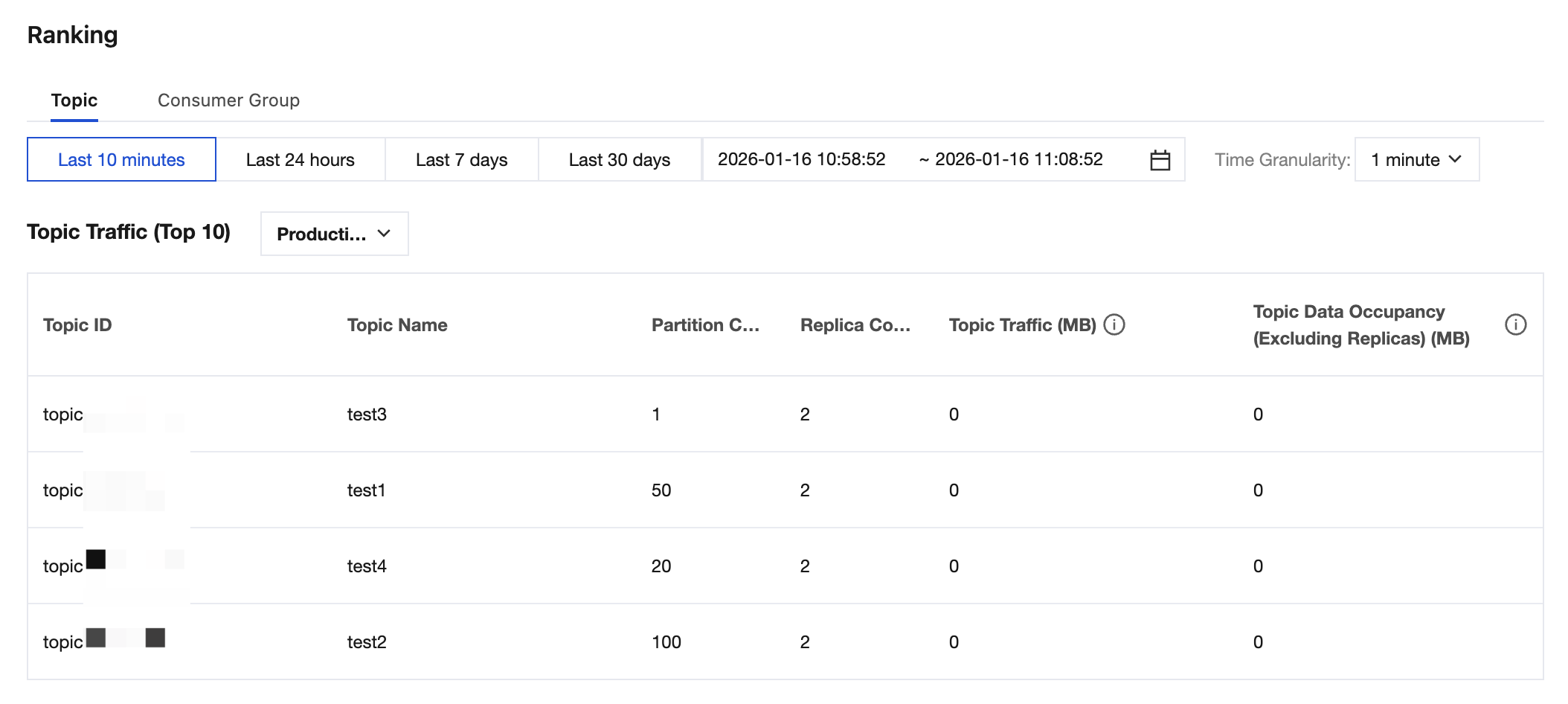
Topic: displays top 10 topics by production/consumption traffic and top 10 topics by occupied disk capacity, and supports viewing topic statistics rankings for specified nodes. This metric helps quickly identify high-load topics and locate issues such as abnormal traffic on a single node or storage overload.Topic: displays top 10 topics by production/consumption traffic and top 10 topics by occupied disk capacity, and supports viewing topic statistics rankings for specified nodes. This metric helps quickly identify high-load topics and locate issues such as abnormal traffic on a single node or storage overload.
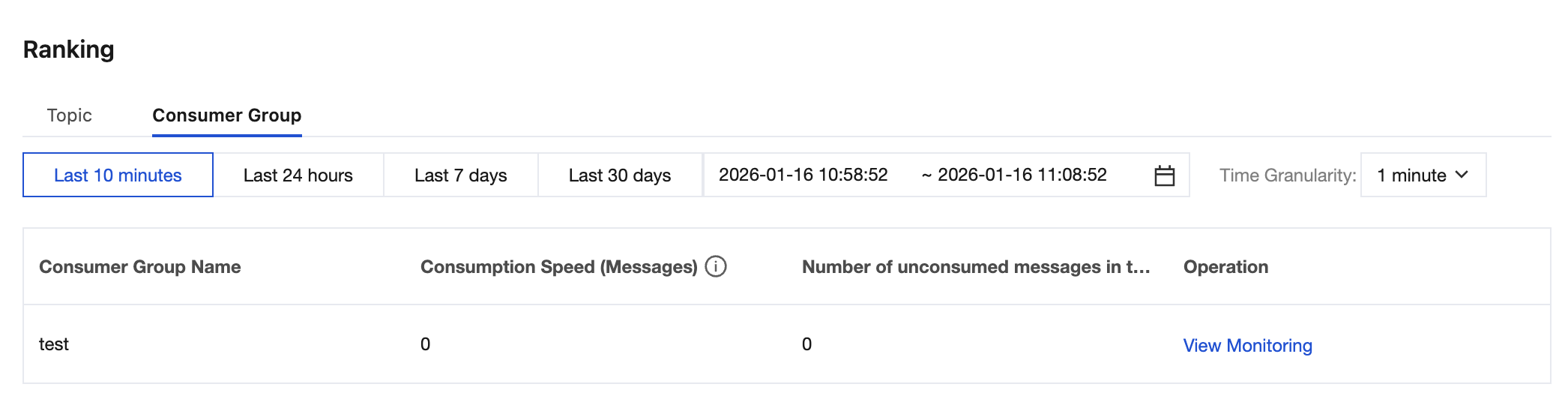
Consumer Group: displays the top 10 consumer groups by consumption rate. This metric helps identify high-throughput consumer groups, locate the consumption delay or backlog issues, and further optimize consumer-side resource allocation.Consumer Group: displays the top 10 consumer groups by consumption rate. This metric helps identify high-throughput consumer groups, locate the consumption delay or backlog issues, and further optimize consumer-side resource allocation.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

