Messages
Last updated:2026-01-20 17:19:23
What Is the Method to Calculate the Number of Remaining Unconsumed Messages?
The calculation method is: Number of unconsumed messages = Maximum offset - Committed offset. As shown in the figure below:
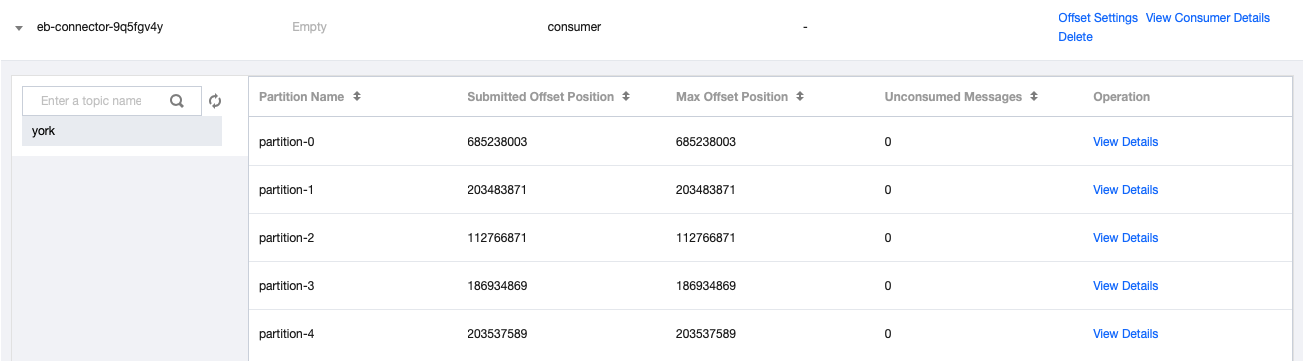
Does TDMQ for CKafka Support Automatic Adjustment of the Message Retention Period?
CKafka supports adding a dynamic message retention policy. After a dynamic data retention policy is set, when disk space utilization reaches a certain percentage, a certain percentage of data will expire automatically to avoid the situation where disk space is used up due to a surge in user messages, leading to the failure to produce and consume messages. For details, see Configuring the Disk Watermark Adjustment Policy.
Why Is the Consumption Offset Not Synchronized to the Server in a Timely Manner?
Issue Symptom
The consumption offset of CKafka is not updated to the server in a timely manner. Therefore, the consumption speed cannot be viewed in the console.
Preliminary Preparations
A CKafka cluster displays the consumption offset by evaluating the consumption speed and offset based on the commit frequency of the client offset. Therefore, when encountering such issues, check the client offset commit status first.
Troubleshooting Guide
Step 1: Checking Whether Production Data Is Being Written
If no consumption backlog and consumption speed have been found, you can check the topic and production monitoring metrics to see whether there is data being written.
1. Go to the console, choose Instance List > ID/Name > Topic List to check whether the end offset of the corresponding topic partition is updated.
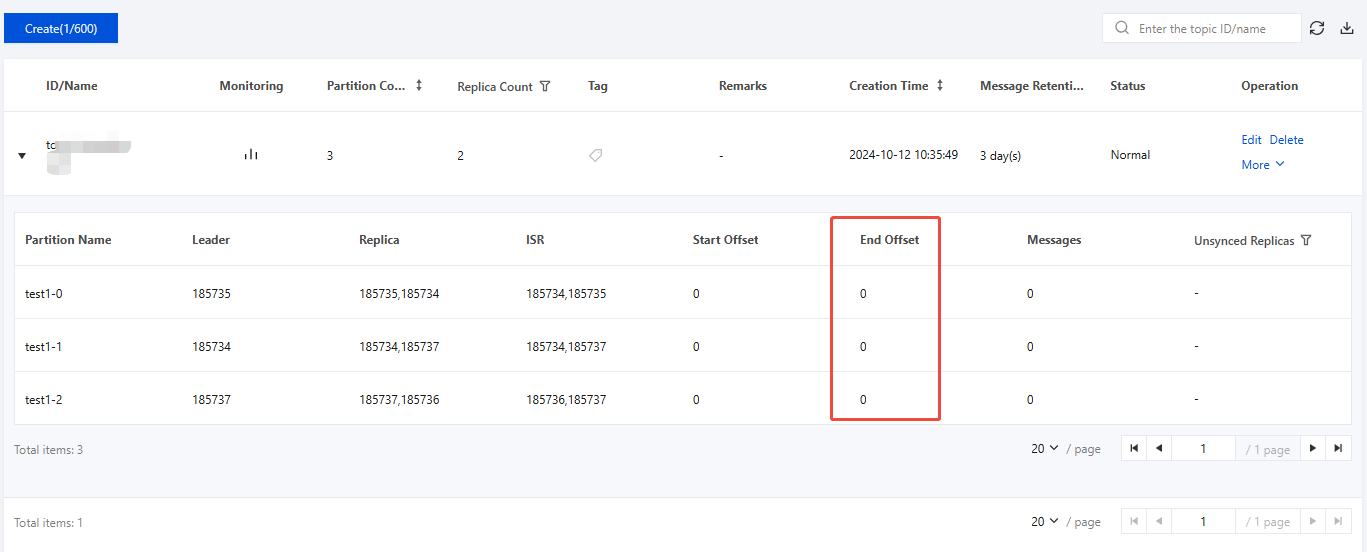
2. Go to the console, choose Instance List > ID/Name > Monitoring > Topic to check whether metrics such as the corresponding production traffic and the total disk space used by messages in the topic are greater than 0.
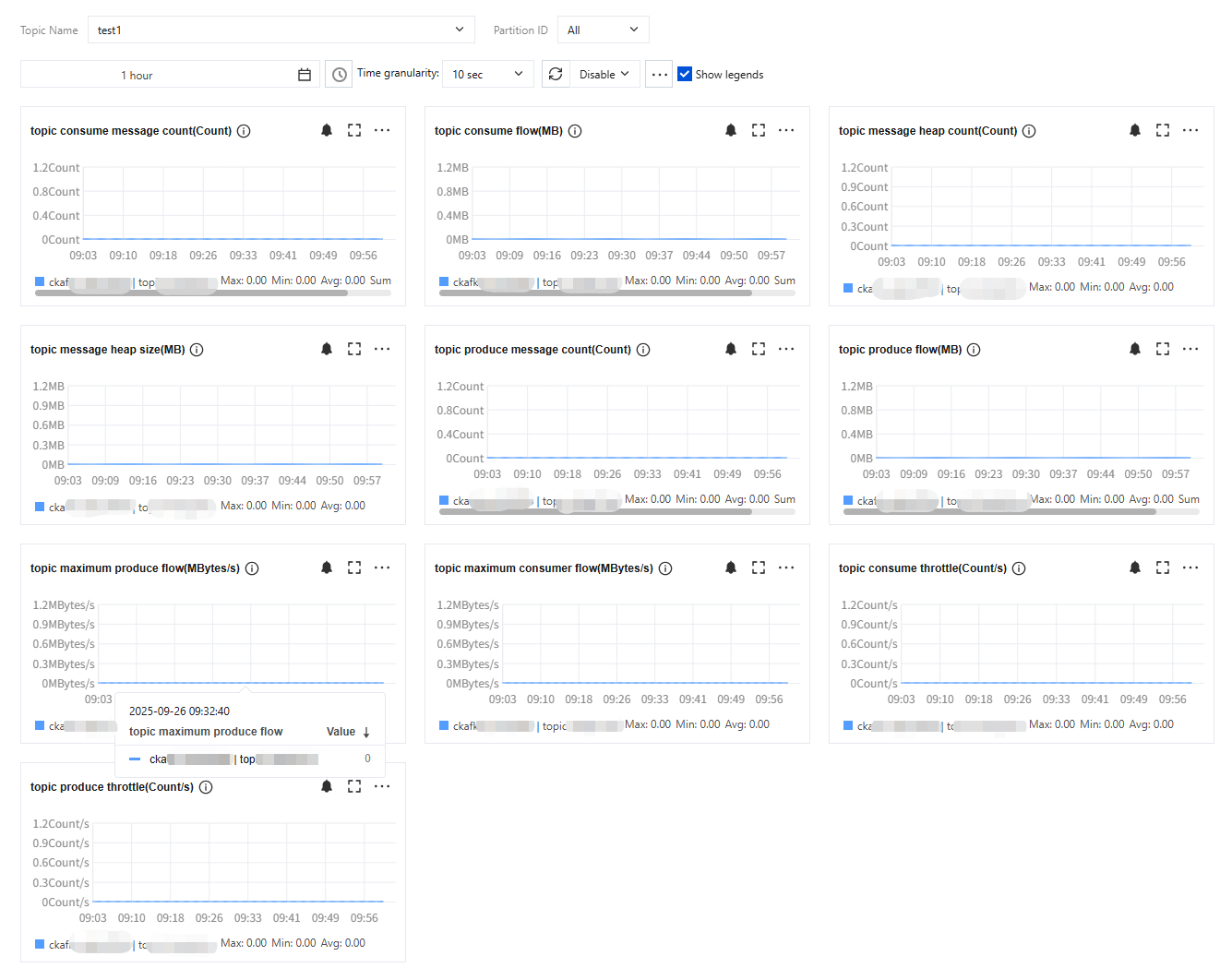
If no real-time data is being written to the topic, there are two possible causes:
If you create a consumer group and set
auto.offset.reset=latest, data will be consumed from the latest offset. Since no real-time data is written to the topic, no offsets will be committed.If the topic data has exceeded the retention period and you set
auto.offset.reset=earliest, data will be consumed from the beginning. Since the data has been retained, no data can be consumed, and no offsets will be committed.In the above cases, no
commit offset behavior occurs. Therefore, the server does not update the consumption offset.Step 2: Checking Client Configurations
For a native Kafka client, you need to check the consumer configurations to see whether automatic commit of
offset: enable.auto.commit is enabled.Native Kafka Java Client Examples
One method is to directly check client configurations. The other method is to search for ConsumerConfig in the program logs, as shown in the figure below. This log is only printed during KafkaConsumer initialization and might not be found if the log retention period is short.

Based on the consumption characteristics of the client, if automatic commit of offsets can be enabled, you can enable this parameter, and the client consumption offset will be updated to the server.
If manual management of offset commits is required, such as when there are stricter requirements for avoiding duplicate consumption or data loss, and
enable.auto.commit is disabled, you need to check whether the client program performs synchronous or asynchronous offset commit operations during consumption, such as consumer.commitSync().while (true) {ConsumerRecords<String, String> consumerRecords = consumer.poll(500);for (ConsumerRecord record : consumerRecords) {System.out.printf("Receive messages: partition:%d, offset:%d, time:%d, key:%s, value:%s\\n", record.partition(), record.offset(), record.timestamp(), record.key(), record.value());}consumer.commitSync();}
After troubleshooting and adjusting the native Kafka client in the above ways, monitor again whether the client consumption offset has been updated to the server.
Flink Used Quite Frequently in Kafka Streaming Scenarios
For the Flink consumption client, its underlying access to Kafka is integrated with the Kafka Source API of Flink and combined with the fault tolerance mechanisms of the Flink framework, such as checkpoint and savepoint mechanisms. This presents two scenarios: underlying processing of enable.auto.commit by the Kafka client and processing of offsets by the Flink checkpoint.
Kafka Source commits the current offset when a checkpoint is completed to ensure that the checkpoint status of Flink is consistent with the committed offsets on the Kafka broker.
If the checkpoint is disabled, Kafka Source relies on the internal logic of the Kafka consumer for periodic and automatic offset committing. This automatic commit feature is configured by the two Kafka consumer configuration items: enable.auto.commit and auto.commit.interval.ms. Note that if users do not actively specify enable.auto.commit in the configuration when using Flink Kafka Source, the Flink framework will set enable.auto.commit to false, which means disabling automatic offset commits. If the Flink checkpoint is disabled, users need to manually enable this parameter.
What Is the Reason That Expired Messages Are Not Deleted in a Timely Manner?
Cause Analysis
The message deletion mechanism of Kafka may result in expired messages not being deleted in a timely manner in certain business scenarios. Lack of understanding of this mechanism can cause confusion. For example, there is a significant gap in message timestamps between Partition 0 and Partition 7, and expired messages in Partition 0 are not being deleted in a timely manner.
Message Deletion Mechanism of Kafka
Kafka stores data on the disk from three dimensions: topics, partitions, and data segments. The conditions for deleting message data are as follows:
Message data is deleted based on the retention period and by data segment.
Each data segment is currently configured as 1 GB in size, and upon reaching 1 GB, it rolls over to generate a new data segment.
A data segment is deleted only when all messages within it have expired.
If a data segment contains a line of message within the retention period, for example, if the last line of the segment file is within the retention period, the segment file will not be deleted.
Due to skewed message writing caused by certain reasons, data writing is concentrated in specific partitions, such as Partition 7; other partitions, such as Partition 0, have minimal data. In this scenario, the data segment in Partition 0 has not reached 1 GB in size. Therefore, it does not roll over. However, since the entire segment contains data in the retention period, messages in Partition 0 will not be deleted.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

