Migration Solution Overview
Last updated:2026-01-20 17:19:21
Scenarios
This document describes feasible solutions for migrating self-built Kafka clusters or those of other cloud vendors to TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) clusters. You can select the most suitable migration method based on your actual business requirements.
Currently, two migration solutions are provided.
1. Use the connector: Use the connector feature provided by CKafka to achieve migration. It supports multiple scenarios, including cloud and off-cloud (cross-cloud and hybrid cloud) scenarios. For details, see Configuring Data Synchronization Between Kafka Instances.
2. Use an open-source tool: Use an open-source tool to complete migration. The specific operation steps of this solution are introduced below.
Migrating with an Open-Source Tool
Solution 1: Single-Producer Dual-Consumer
This solution is overall simple, clear, and easy to follow. It involves no data backlog and enables a smooth transition.
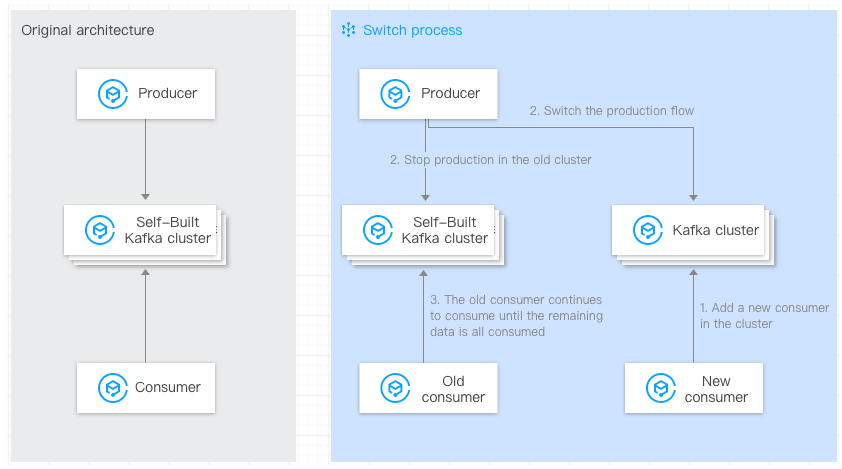
Approach:
2. The existing consumers in the self-built Kafka cluster remain unchanged.
3. Start a new consumer on the CKafka client, configure the bootstrap-server of the new CKafka cluster, and consume data from the new CKafka cluster.
4. Wait until all consumers have listened to the new CKafka cluster.
5. Switch the production of the self-built cluster to the new CKafka cluster (configure the bootstrap-server of the new CKafka cluster).
6. The existing consumers in the self-built Kafka cluster continue to consume the remaining data in the self-built Kafka cluster, and the original consumers can only be taken offline when all the data has been consumed.
Advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages: The overall migration process is simple, clear, and easy to follow. It involves no data backlog and enables a smooth transition.
Disadvantages: An additional consumer is required.
Solution 2: Single-Producer Single-Consumer
This solution is overall simple, clear, and easy to follow.
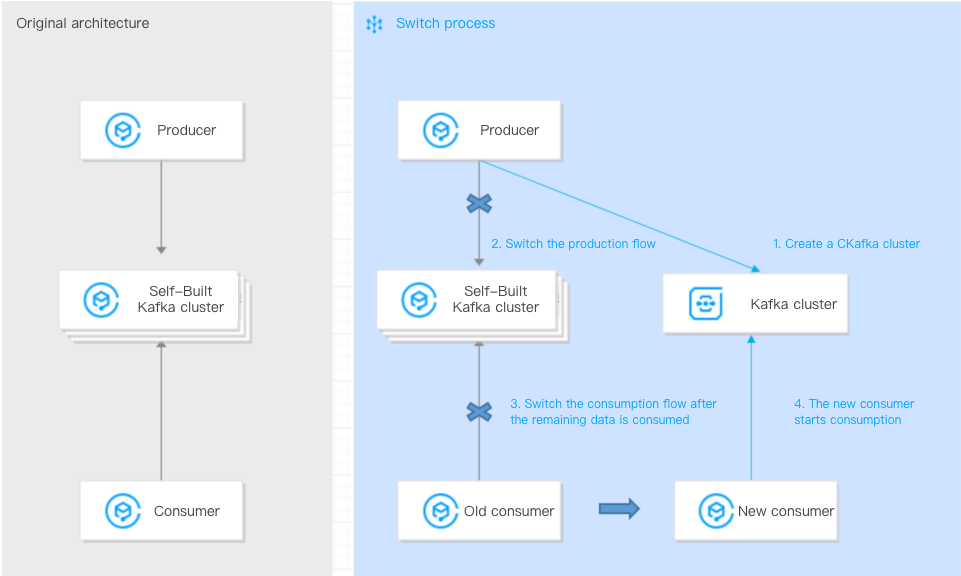
Approach:
2. Switch the production of the self-built Kafka cluster to the new CKafka cluster (configure the bootstrap-server of the new CKafka cluster).
3. Wait for the consumers in the self-built cluster to finish consuming the remaining data.
4. Switch the existing consumers to consume data from the new CKafka cluster (configure the bootstrap-server of the new CKafka cluster).
Advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages: The overall migration process is simple, clear, and easy to follow. It enables a smooth transition.
Disadvantages: After production is switched to the CKafka cluster and before the existing consumers are switched to the CKafka cluster, a certain amount of message backlog may accumulate in the CKafka cluster.
Solution 3: Migrating with Mirrormaker
This solution involves migrating the existing data from a self-built Kafka cluster to a CKafka cluster.
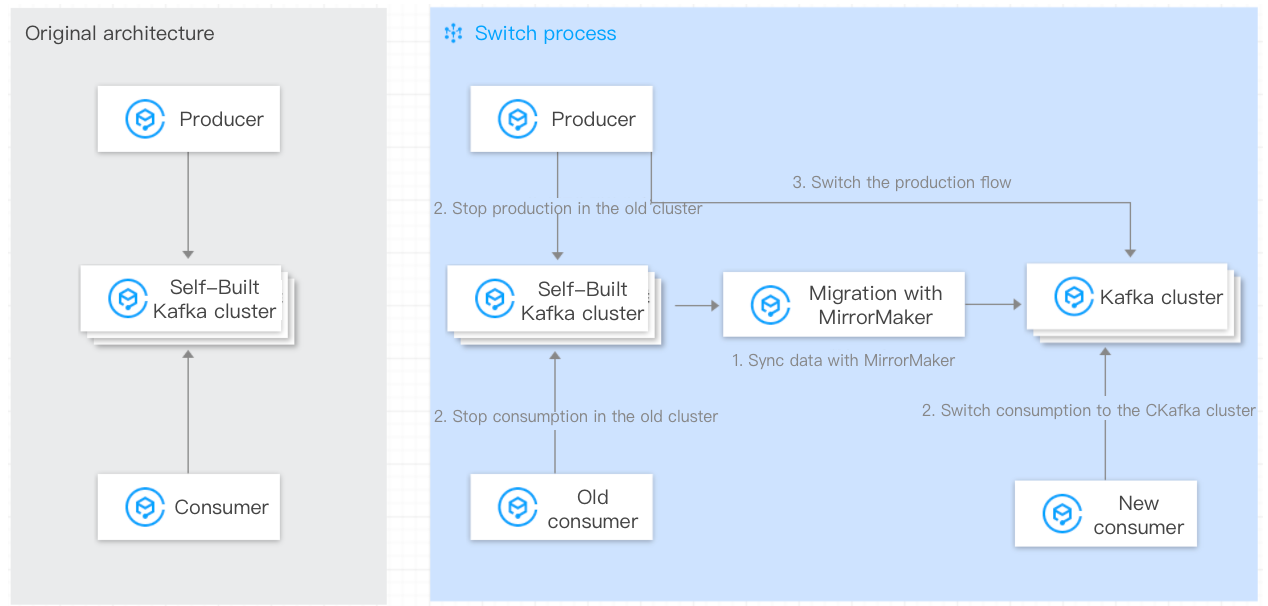
Approach:
2. The existing consumers in the self-built Kafka cluster remain unchanged.
3. Start the data synchronization feature of the Mirrormaker tool.
4. Wait for data synchronization to complete, modify consumer configurations, and switch the consumers.
5. Wait for data synchronization to complete, modify producer configurations, and switch the producer.
6. Migration is completed.
Advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages: The overall migration process is simple, clear, and easy to follow, allowing historical data to be synchronized to the CKafka cluster.
Disadvantages: After being switched to the target cluster, the consumers need to start consuming data from the beginning. Consumption idempotence is required.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

